Written by Mike Szczys, Zephyr Ambassador and Developer Relations Engineer at Golioth
This blog originally ran on the Golioth website. For more content like this, click here.
In April, I programmed 15 consecutive boards with unique firmware images. I needed to build multiple versions of the same Zephyr firmware, supplying unique values to each process during build time. The Zephyr Kconfig system provides built-in support for passing values during a build. The trick is that you can’t just dynamically declare symbols, you need to tell Zephyr that you are expecting a value to be set for a new symbol. Today I will walk through how to do this, and why you might want to.
Fifteen Devices, Fifteen Names
In my case I was pre-provisioning devices to use in a training workshop. I supplied each build them with credentials so they would be able to authenticate with the Golioth Cloud platform. There is already built-in Kconfig support for these values. But at the same time, I wanted the devices to have a human-readable name that matches up with the device displayed on our cloud console. During the training, the device prints its name on a screen as an easy reference.
The solution to both of these needs is to set the values at build time using the -D<SYMBOLNAME>=flag format on the command line. Any Kconfig value that you would normally set in a prj.conf file can also be set this way. So if you wanted to enable the Zephyr Logging subsystem for just one build, you could turn it on by adding -DCONFIG_LOG=y to your west build command.
I used a script that called the goliothctl command line tool to create each device and to make the credentials for each on our cloud platform. The script then called the west tool to build the firmware, supplying the device name and the credentials as arguments.
The gotcha is that if you try to make up your own symbols on the fly (like -DGOLIOTH_IS_AWESOME=y) you will be met with errors. Zephyr needs to know what symbols to expect–anything else is assumed to be a typo.
Add a Custom Symbol to Zephyr Kconfig
The easiest way to add a symbol is to declare it in the Kconfig file in your project directory. The syntax for this is pretty simple:
- config SYMBOLNAME
- bool “Description”
According to the Linux docs, the following types are valid: bool, tristate, string, hex, int. The description string is important if you want the value to appear in menuconfig. Consider the following code:
config GOLIOTH_IS_AWESOME
bool "Confirm that Golioth is awesome"
config MAGTAG_NAME
string "MagTag Name"
default "MagTag-One"
help
Used during automatic provisioning for workshops
This creates two new symbols, one accepts a boolean value, the other a string value. These can be viewed and set using the menuconfig interface. After building your project, type west build -t menuconfig.
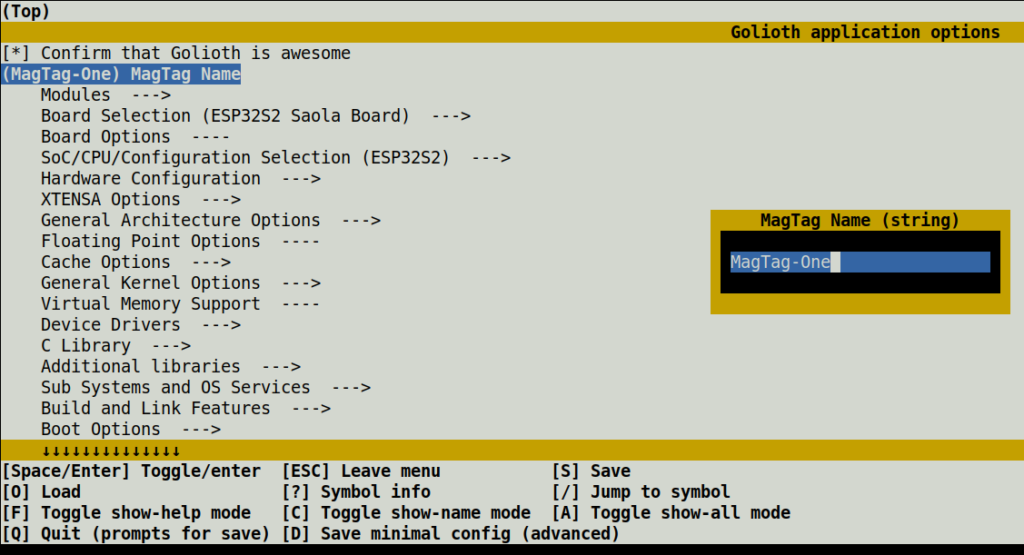
Both of the new symbols appear in the menu, and you can see the strings we used when declaring the type are what is shown as labels in the menu interface. Of course, you can now set the values in a Kconfig file as you would any other interface. But for me, the goal was to do so from the command line. Here is an example build command used by my provisioning script:
west build -b esp32s2_saola magtag-demo -d /tmp/magtag-build -DCONFIG_MAGTAG_NAME=\"azure-camellia\" -DCONFIG_GOLIOTH_SYSTEM_CLIENT_PSK_ID=\"azure-camellia-id@developer-training\" -DCONFIG_GOLIOTH_SYSTEM_CLIENT_PSK=\"b00a0fef769d65d9021d747c8d710af5\" -DCONFIG_ESP32_WIFI_SSID=\"Golioth\" -DCONFIG_ESP32_WIFI_PASSWORD=\"training\"
The symbol will now be available to your c code:
LOG_INF("Device name: %s", CONFIG_MAGTAG_NAME);
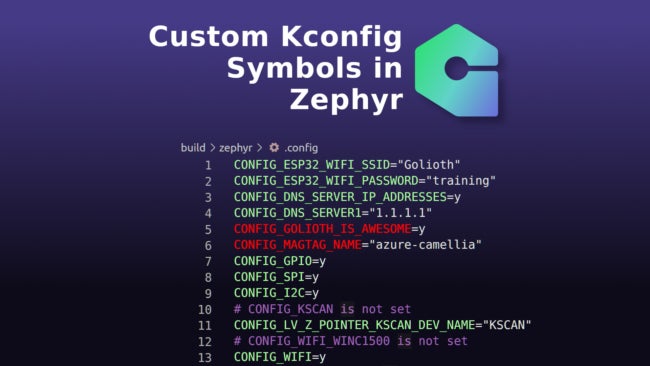
And of course you can view the state of all Kconfig symbols processed during the build process. Just open up the build/zephyr/.config file that was generated. Below you will see the first baker’s-dozen lines, including my custom symbols along with some specified by the Golioth SDK, and others that are standard to Zephyr:
CONFIG_ESP32_WIFI_SSID="Golioth"
CONFIG_ESP32_WIFI_PASSWORD="training"
CONFIG_DNS_SERVER_IP_ADDRESSES=y
CONFIG_DNS_SERVER1="1.1.1.1"
CONFIG_GOLIOTH_IS_AWESOME=y
CONFIG_MAGTAG_NAME="azure-camellia"
CONFIG_GPIO=y
CONFIG_SPI=y
CONFIG_I2C=y
# CONFIG_KSCAN is not set
CONFIG_LV_Z_POINTER_KSCAN_DEV_NAME="KSCAN"
# CONFIG_WIFI_WINC1500 is not set
CONFIG_WIFI=y
Learn more about Kconfig
To dive deeper into Kconfig options, your first stop should be the Zephry Docs page on Setting Kconfig values. I also found the Kconfig Tips and Best Practices to be useful, as well as the Linux Kconfig Language reference. Ten minutes of reading the docs, and a little bit of trial and error, and you’ll have a good grasp of what Kconfig is all about.